History notes for medieval history.
1. Source
2. 1206 to 1556
3. 1556 to 1761
4. Vijaynagar.
Contents
- 1 Unit 1: Source of Medieval Indian History (मध्यकालीन भारतीय इतिहास का स्रोत)
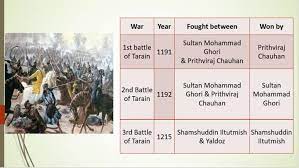
- 2 Unit 2: Delhi Sultanate 1206 to 1556 (दिल्ली सल्तनत 1206 से 1556)
- 3 Unit 3: Mughal Period 1526 to 1761 ( मुग़ल काल 1526 से 1761)
- 4
- 5 Unit 4: Vijaynagar Empire
- 5.0.1 🧠 History Subsidiary – Last Minute Study (Quick Revision Guide)
- 5.0.2 📚 1. Ancient India – Key Points
- 5.0.3 🕌 2. Medieval India – Key Points
- 5.0.4 🇮🇳 3. Modern India – Highlights
- 5.0.5 🌍 4. World History (if included)
- 5.0.6 📝 Smart Tips for Exam Revision
- 5.0.7 ⏱️ Must-Read Topics (High Weightage)
- 5.0.8 gs prelims (2025 -2025) – modern indian history
- 5.0.9 History Subsidiary – Last Minutes Study
- 5.0.10 History-Paper-I.pdf
Unit 1: Source of Medieval Indian History (मध्यकालीन भारतीय इतिहास का स्रोत)

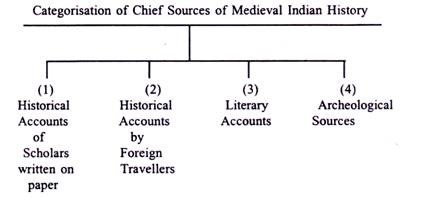
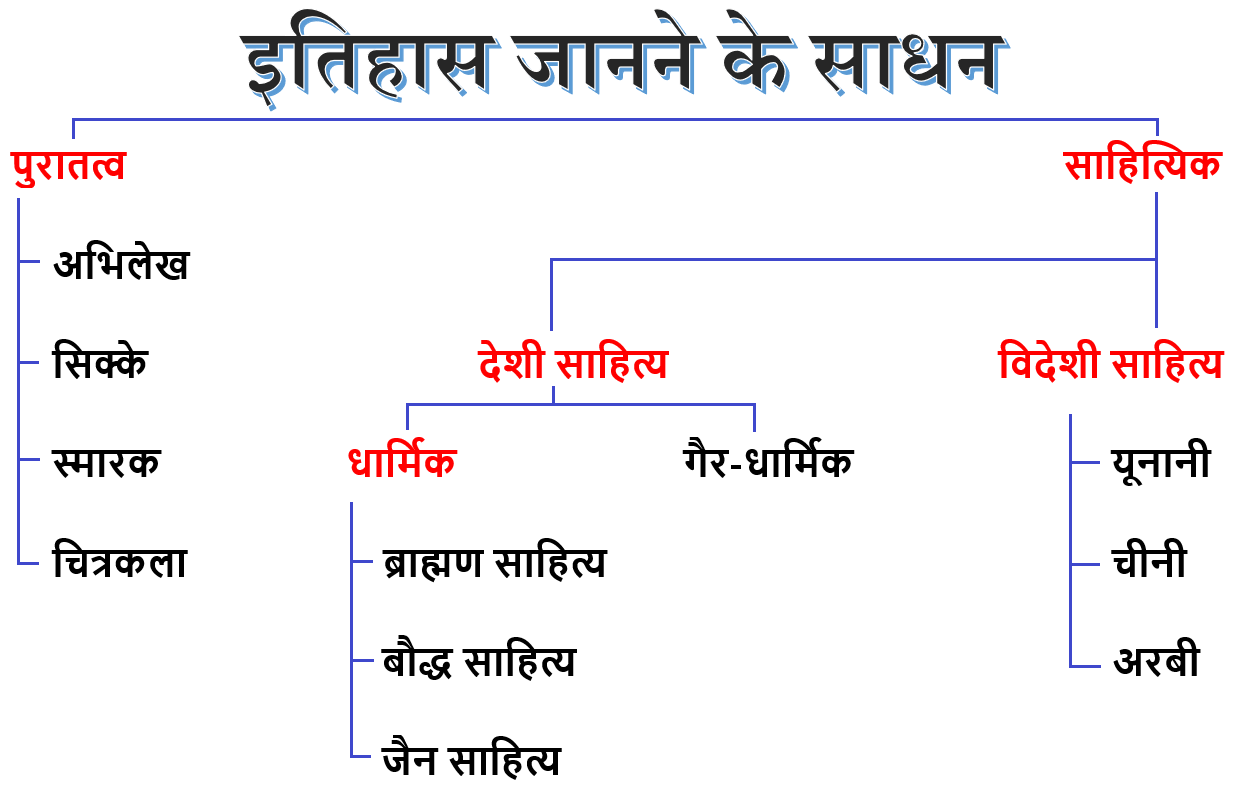
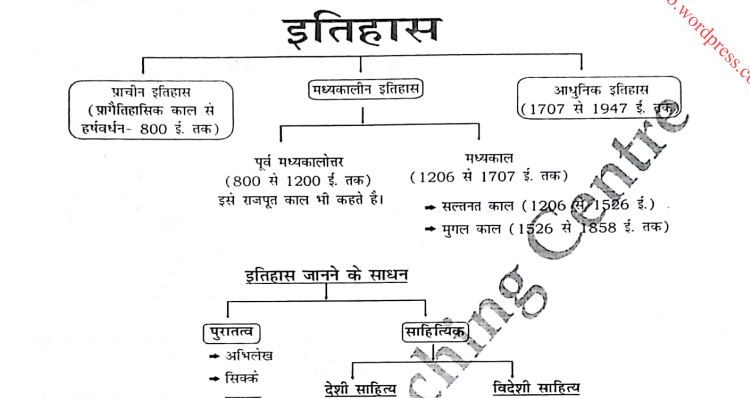
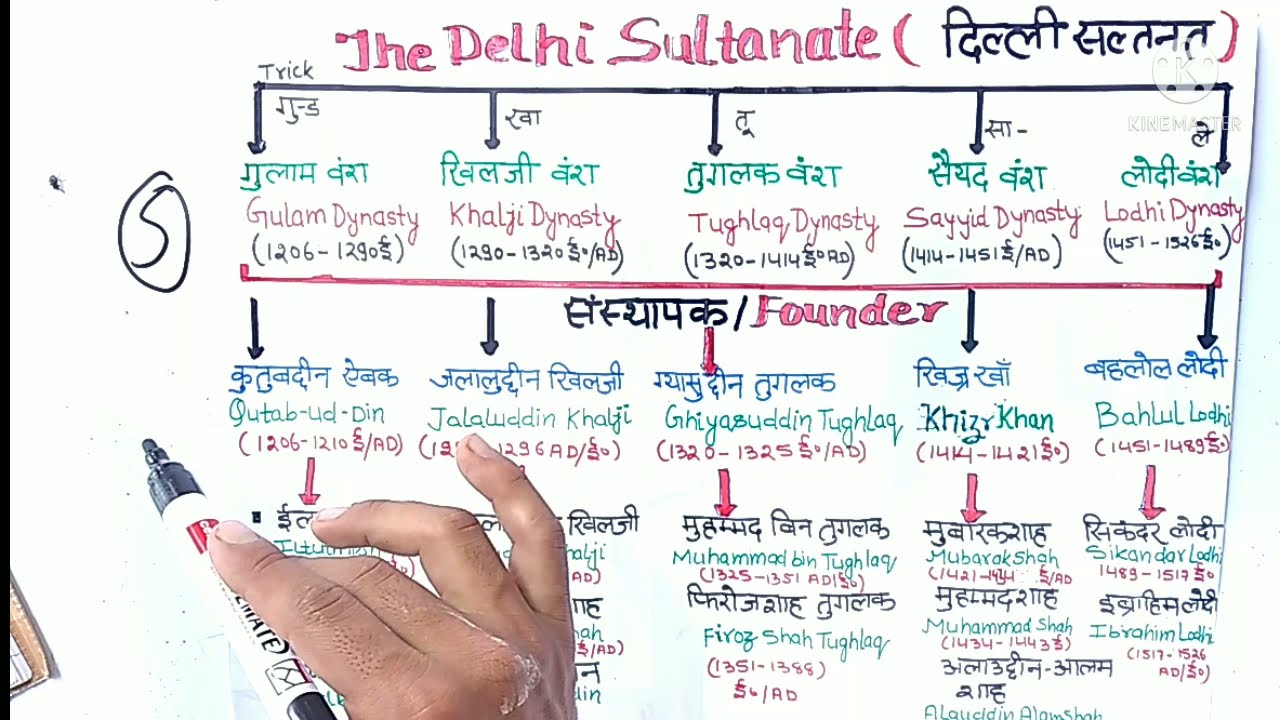
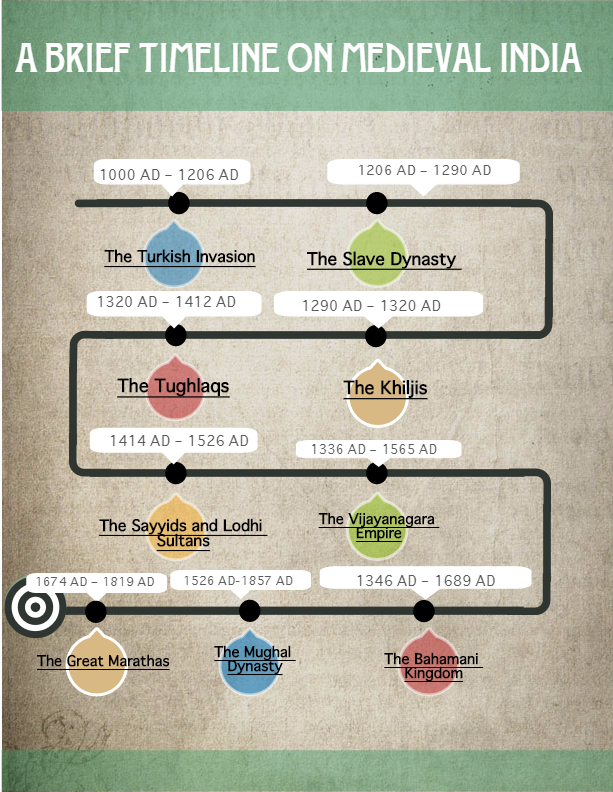
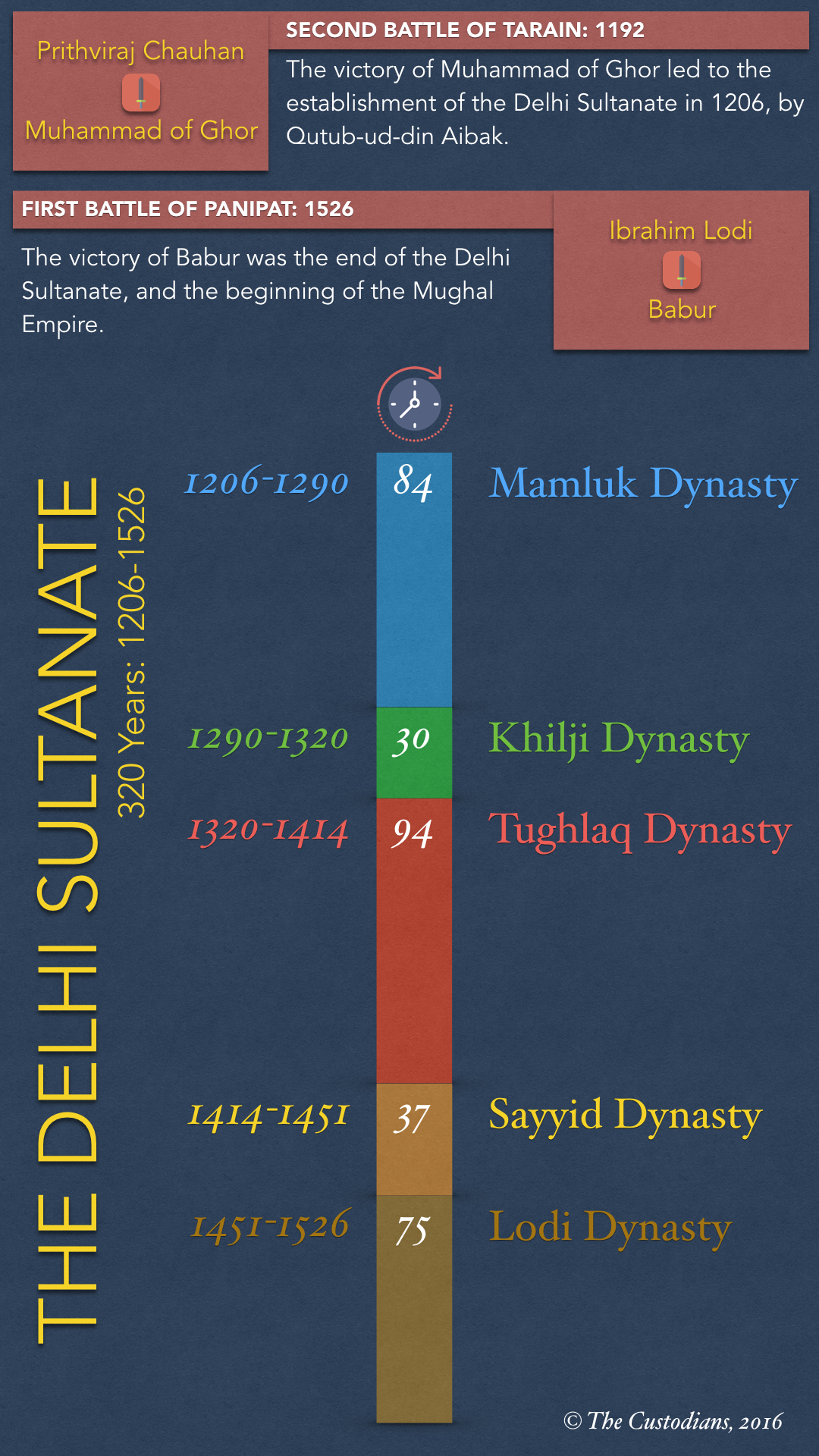
Unit 2: Delhi Sultanate 1206 to 1556 (दिल्ली सल्तनत 1206 से 1556)












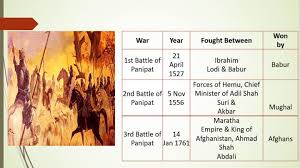
Unit 3: Mughal Period 1526 to 1761 ( मुग़ल काल 1526 से 1761)








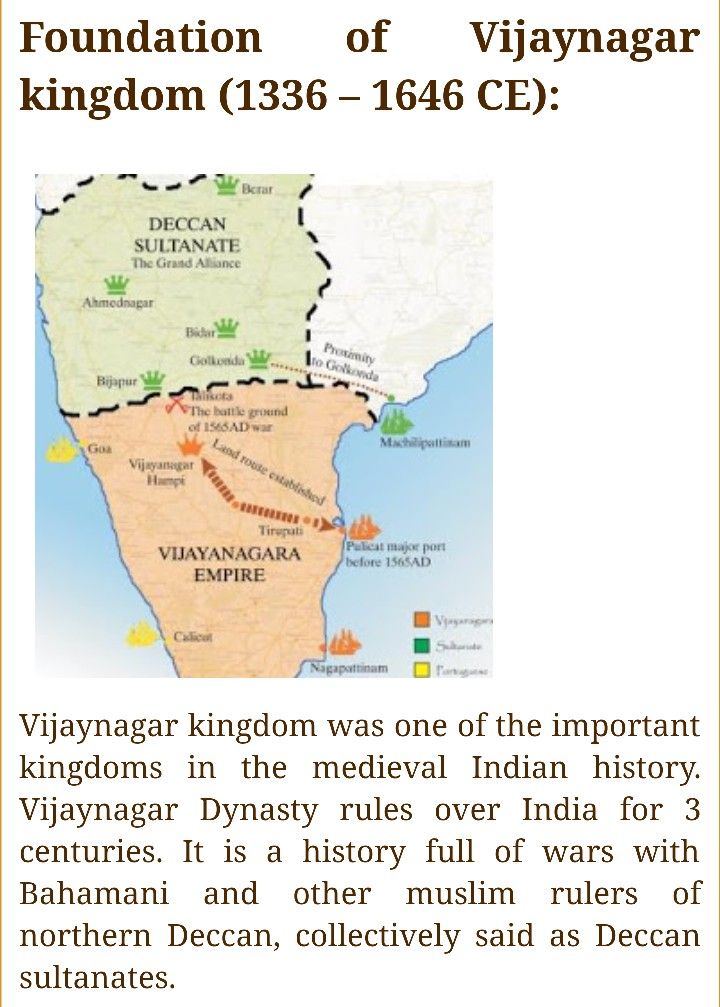
Unit 4: Vijaynagar Empire

Here’s a Last-Minute Study Guide for your History Subsidiary subject—perfect for quick revision before exams! It’s structured to help you recall key topics, important events, and smart keywords fast.
🧠 History Subsidiary – Last Minute Study (Quick Revision Guide)
📚 1. Ancient India – Key Points
- Indus Valley Civilization (3300–1300 BCE)
- Urban planning (Grid system, drainage)
- Harappa & Mohenjodaro
- Script undeciphered
- Vedic Age
- Early Vedic (Rigveda): Pastoral society
- Later Vedic: Agriculture, caste system began
- Mauryan Empire (322–185 BCE)
- Chandragupta Maurya
- Ashoka (Kalinga War, Dhamma, Edicts)
- Gupta Empire (320–550 CE)
- Golden Age of India: Science, Literature (Kalidasa), Art
- Decline due to Hun invasions
🕌 2. Medieval India – Key Points
- Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526)
- Dynasties: Slave → Khilji → Tughlaq → Sayyid → Lodi
- Alauddin Khilji: Market control, South India expansion
- Muhammad bin Tughlaq: Token currency, failed policies
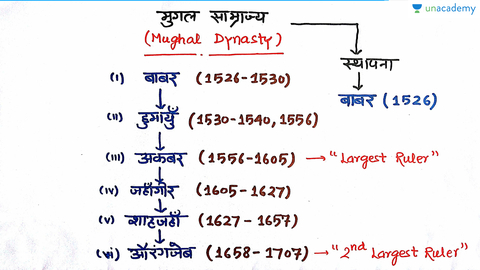
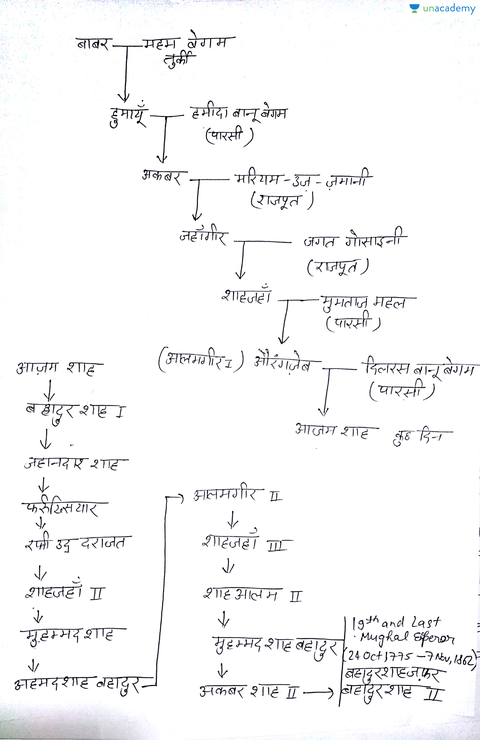
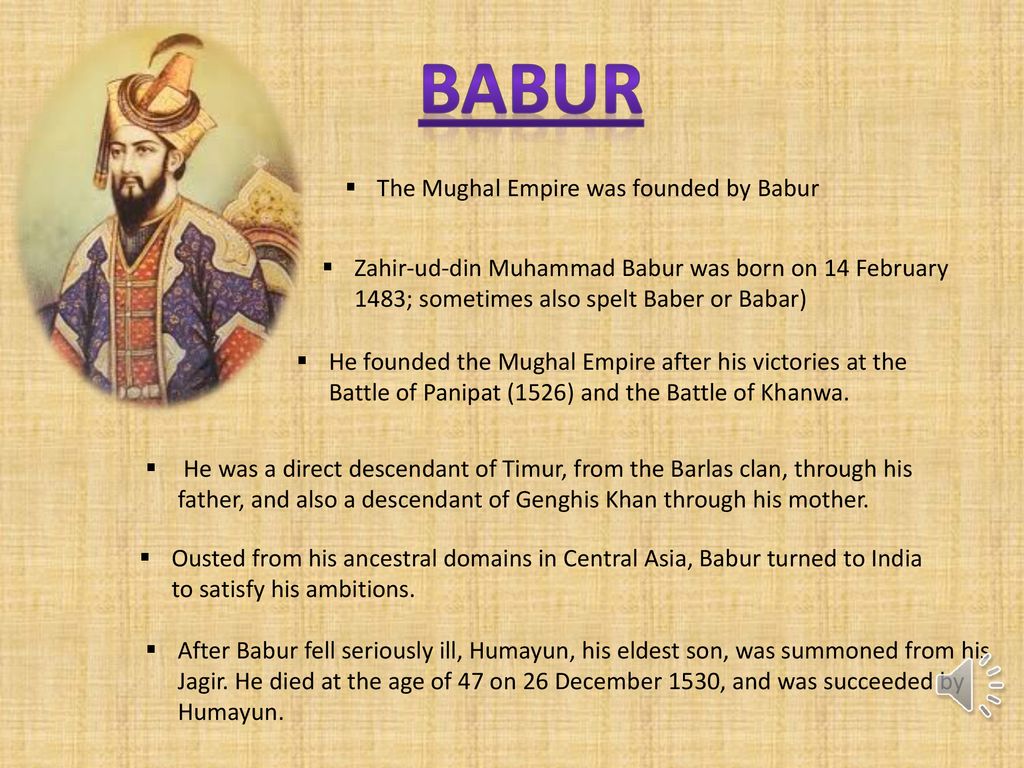
- Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
- Babur → Humayun → Akbar → Jahangir → Shah Jahan → Aurangzeb
- Akbar’s policies: Sulh-i-Kul, Mansabdari system
- Art & Architecture: Red Fort, Taj Mahal
- Decline: Weak successors + British interference
🇮🇳 3. Modern India – Highlights
- British East India Company
- Battle of Plassey (1757), Buxar (1764)
- Regulating Act 1773, Pitt’s India Act 1784
- Revolt of 1857
- Causes: Political, economic, religious
- Leaders: Mangal Pandey, Rani Lakshmi Bai, Bahadur Shah Zafar
- Result: Crown Rule began (British Raj)
- Indian National Movement
- Early Phase: Moderates vs Extremists
- 1919 – Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
- 1920 – Non-Cooperation Movement
- 1930 – Civil Disobedience, Salt March
- 1942 – Quit India Movement
- 1947 – Independence, Partition
🌍 4. World History (if included)
- French Revolution (1789)
- Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
- End of monarchy → rise of Napoleon
- Industrial Revolution (18th Century)
- Shift from manual to machine
- Origin: Britain
- Social effects: Urbanization, child labor
- World Wars
- WWI (1914–1918): Assassination of Archduke
- WWII (1939–1945): Hitler, Holocaust, Hiroshima
- Formation of UNO (1945)
📝 Smart Tips for Exam Revision
✅ Revise timelines & dates
✅ Use flowcharts for empires/rulers
✅ Focus on cause-effect format for revolts and wars
✅ Learn 1–2 points on each personality
✅ Use keywords: “Dhamma”, “Mansabdari”, “Drain of Wealth”, “Permanent Settlement”
⏱️ Must-Read Topics (High Weightage)
| Topic | Why Important |
|---|---|
| 1857 Revolt | Foundation of modern nationalism |
| Akbar’s Administration | Appears in every paper |
| British Economic Policies | Causes of poverty & unrest |
| Gandhi’s Movements | Chronology & impact |
| French/Industrial Rev. | Often asked in comparison format |
Would you like:
- A PDF printable revision sheet?
- Sample previous year questions?
- Important map-based topics?
Let me know and I’ll prepare it quickly for you!

